 |
 |
| Ann Optom Contact Lens > Volume 21(1); 2022 > Article |
|
Abstract
ņĄ£ĻĘ╝ ņĢłĻĄ¼Ļ▒┤ņĪ░ņ”ØņØś ļ░£ļ│æĻĖ░ņĀäņŚÉ Ļ░üļ¦ēņŗĀĻ▓ĮņØś ņŚŁĒĢĀņØ┤ ļČĆĻ░üļÉśĻ│Ā ņ׳ļŗż. ņŗĀĻ▓ĮĒÄ®Ēŗ░ļō£Ļ░Ć ņŗĀĻ▓ĮĻ│äņÖĆ ļ®┤ņŚŁĻ│äņØś ņżæņÜöĒĢ£ ļ¦żĻ░£ņ▓┤ļĪ£ ņĢīļĀżņĀĖ ņ׳ļŗżļŖö ņĀÉņØä Ļ│ĀļĀżĒĢśļ®┤, ņŗĀĻ▓Į ļ¦Éļŗ©ņŚÉņä£ ļČäļ╣äļÉśļŖö ņŗĀĻ▓ĮĒÄ®Ēŗ░ļō£Ļ░Ć ņ£Āļ░£ĒĢśĻ│Ā ņĪ░ņĀłĒĢśļŖö ņŗĀĻ▓Įņä▒ņŚ╝ņ”ØņØĆ ņĢłĻĄ¼Ļ▒┤ņĪ░ņ”ØņØś ļ░£ļ│æĻĖ░ņĀäņŚÉļÅä Ļ┤ĆņŚ¼ĒĢĀ Ļ▓āņ£╝ļĪ£ ĻĖ░ļīĆļÉ£ļŗż. ņĄ£ĻĘ╝ņŚÉ ļłł ņłśņłĀ ļ░Å ņĮśĒāØĒŖĖļĀīņ”ł ņé¼ņÜ® ĒøäņŚÉ ļ░£ņāØĒĢśļŖö ņĢłĻĄ¼Ļ▒┤ņĪ░ņ”ØņŚÉ ļīĆĒĢ£ Ļ┤Ćņŗ¼ņØ┤ ņ”ØĻ░ĆĒĢśļ®┤ņä£, ņØśņØĖņä▒ ņĢłĻĄ¼Ļ▒┤ņĪ░ņ”ØņØĆ ņĢłĻĄ¼Ļ▒┤ņĪ░ņ”ØņØś ņżæņÜöĒĢ£ ļČäņĢ╝ļĪ£ Ļ░üĻ┤æņØä ļ░øĻ│Ā ņ׳ļŗż. ņØ┤ ļģ╝ļ¼ĖņŚÉņä£ļŖö ņĢłĻĄ¼Ļ▒┤ņĪ░ņ”ØņØś ļ░£ļ│æĻĖ░ņĀäĻ│╝ Ļ┤ĆļĀ©ĒĢśņŚ¼ ņŗĀĻ▓ĮĒÄ®Ēŗ░ļō£ņØś ņŚŁĒĢĀņŚÉ ļīĆĒĢ£ ņĄ£ĻĘ╝ ņŚ░ĻĄ¼ Ļ▓░Ļ│╝ļōżņØä Ļ░äļŗ©Ē׳ ņé┤ĒÄ┤ļ│┤Ļ│Ā, ĒŖ╣Ē׳ ņØśņØĖņä▒ ņĢłĻĄ¼Ļ▒┤ņĪ░ņ”ØņŚÉņä£ ņŗĀĻ▓ĮĒÄ®Ēŗ░ļō£ņØś ļ│ĆĒÖö ļ░Å Ļ░ĆļŖźĒĢ£ ņŚŁĒĢĀņŚÉ ļīĆĒĢ£ ĻĖ░ņĪ┤ ņŚ░ĻĄ¼ Ļ▓░Ļ│╝ļōżņØä ņĀĢļ”¼ĒĢśĻ│Āņ×É ĒĢ£ļŗż.
Abstract
Recently, the role of the corneal nerve in the pathogenesis of dry eye disease (DED) has been highlighted. Considering that neuropeptides are known as important mediators between the nervous and immune systems, neurogenic inflammation induced and regulated by neuropeptides secreted from nerve terminals is expected to be involved in the pathogenesis of DED. And iatrogenic DED has been recently spotlighted as an important field with increasing interest in DED that occurs after ocular surgery or contact lens use. In this paper, recent studies on the role of neuropeptides in the pathogenesis of DED, in particular, the changes and possible roles of neuropeptides in iatrogenic DED were reviewed.
ņÜ░ļ”¼ ļ¬ĖņØĆ ĻĖ░Ļ│äņĀü ņåÉņāüņØ┤ļéś ļ│æņøÉņ▓┤ņØś ņ╣©ņ×ģņŚÉ ļīĆĒĢŁĒĢśĻĖ░ ņ£äĒĢ£ ņŗ£ņŖżĒģ£ņØä Ļ░¢ņČöĻ│Ā ņ׳ļŖöļŹ░, ļ®┤ņŚŁĻ│äņÖĆ ņŗĀĻ▓ĮĻ│äĻ░Ć ņāüĒśĖņ×æņÜ®ņØä ĒåĄĒĢśņŚ¼ ņØ┤ļ¤¼ĒĢ£ ņŚŁĒĢĀņØä ļ¦ĪĻ▓ī ļÉ£ļŗż[1]. ņØ┤ Ļ│╝ņĀĢņŚÉņä£ ļ®┤ņŚŁĻ│äņÖĆ ņŗĀĻ▓ĮĻ│ä ņāüĒśĖņ×æņÜ®ņŚÉ ņżæņÜöĒĢ£ ņŚŁĒĢĀņØä ĒĢśļŖö ņŗĀĻ▓ĮĒÄ®Ēŗ░ļō£(neuropeptide), ņØ┤ļź╝ ĒåĄĒĢśņŚ¼ ņ£Āļ░£ļÉśĻ│Ā ņĪ░ņĀłļÉśļŖö ņŗĀĻ▓Įņä▒ņŚ╝ņ”Ø(neurogenic inflammation)ņØ┤ ņżæņÜöĒĢ£ ņŚŁĒĢĀņØä ĒĢ£ļŗż[2-5]. ĒĢśņ¦Ćļ¦ī ņØ┤ļ¤¼ĒĢ£ ņŗĀĻ▓Įņä▒ņŚ╝ņ”ØņØĆ ņØ╝ļČĆ ņ¦łĒÖśņŚÉņä£ļŖö ņ¦łĒÖśņØä ņ£Āļ░£ĒĢśļŖö ĻĖ░ņĀäņ£╝ļĪ£ ņ×æņÜ®ĒĢĀ ņłśļÅä ņ׳ņØīņØ┤ ļ│┤Ļ│ĀļÉśĻ│Ā ņ׳Ļ│Ā[5-10], ņĢłĻĄ¼Ļ▒┤ņĪ░ņ”ØņØś ļ░£ļ│æĻĖ░ņĀäņŚÉļÅä Ļ┤ĆņŚ¼ĒĢĀ Ļ░ĆļŖźņä▒ļÅä ņśżļל ņĀäļČĆĒä░ ņĀ£ņŗ£ļÉśņŚłļŗż[2,11-13]. ņĄ£ĻĘ╝ņŚÉ ļłł ņłśņłĀ ļ░Å ņĮśĒāØĒŖĖļĀīņ”ł ņé¼ņÜ® ĒøäņŚÉ ļ░£ņāØĒĢśļŖö ņĢłĻĄ¼Ļ▒┤ņĪ░ņ”ØņŚÉ ļīĆĒĢ£ Ļ┤Ćņŗ¼ņØ┤ ņ”ØĻ░ĆĒĢśļ®┤ņä£, ņØśņØĖņä▒ ņĢłĻĄ¼Ļ▒┤ņĪ░ņ”ØņØĆ Tear Film & Ocular Surface SocietyņØś ĻĄŁņĀ£ņĢłĻĄ¼Ļ▒┤ņĪ░ņ”ØņøīĒü¼ņłŹ II (International Dry Eye Workshop II)ņŚÉņä£ ļÅģļ”ĮļÉ£ ņŻ╝ņĀ£ļĪ£ ļŗżļŻ©ņ¢┤ņ¦ł ņĀĢļÅäļĪ£ Ļ░üĻ┤æņØä ļ░øĻ│Ā ņ׳ļŖö ļČäņĢ╝ņØ┤ļŗż[14]. ņØ┤ ļģ╝ļ¼ĖņŚÉņä£ļŖö ņĢłĻĄ¼Ļ▒┤ņĪ░ņ”ØņØś ļ░£ļ│æĻĖ░ņĀäĻ│╝ Ļ┤ĆļĀ©ĒĢśņŚ¼ ņŗĀĻ▓ĮĒÄ®Ēŗ░ļō£ņØś ņŚŁĒĢĀņŚÉ ļīĆĒĢ£ ņĄ£ĻĘ╝ ņŚ░ĻĄ¼ Ļ▓░Ļ│╝ļōżĻ│╝ ĒŖ╣Ē׳ ņØśņØĖņä▒ ņĢłĻĄ¼Ļ▒┤ņĪ░ņ”ØņŚÉņä£ ņŗĀĻ▓ĮĒÄ®Ēŗ░ļō£ņØś ļ│ĆĒÖöļź╝ ļ│Ė ļģ╝ļ¼ĖļōżņØä Ļ│Āņ░░ĒĢśņŚ¼ Ē¢źĒøä ņØ┤ ļČäņĢ╝ ņŚ░ĻĄ¼ņØś ļ░®Ē¢źņØä ņĀ£ņŗ£ĒĢśĻ│Āņ×É ĒĢ£ļŗż.
ņÜ░ļ”¼ ļ¬ĖņØĆ ņÖĖļČĆņŚÉņä£ ļōżņ¢┤ņśżļŖö ĻĖ░Ļ│äņĀü ņåÉņāüņØ┤ļéś ļ│æņøÉņ▓┤ņØś ņ╣©ņ×ģņŚÉ ļīĆĒĢŁĒĢśĻĖ░ ņ£äĒĢ£ ņŗ£ņŖżĒģ£ņØä Ļ░¢ņČöĻ│Ā ņ׳ņ£╝ļ®░ ļłłļÅä ņśłņÖĖļŖö ņĢäļŗłļŗż[1]. ļ®┤ņŚŁ Ļ┤ĆņÜ®ņØ┤ ņל ņĢīļĀżņ¦ä ņĀäļ░®Ļ│╝ļŖö ļŗ¼ļ”¼, ļłł Ēæ£ļ®┤ņŚÉņä£ļÅä ņØ┤ļ¤¼ĒĢ£ ņåÉņāüĻ│╝ ļ│æņøÉņ▓┤ņŚÉ ļīĆĒĢ£ ļüŖņ×äņŚåļŖö Ļ░Éņŗ£Ļ░Ć ņØ┤ļŻ©ņ¢┤ņ¦ĆĻ│Ā ņ׳ņ£╝ļ®░, ņØ┤ Ļ│╝ņĀĢņŚÉņä£ ņŗĀĻ▓Įņä▒ņŚ╝ņ”ØņØ┤ ņżæņÜöĒĢ£ ņŚŁĒĢĀņØä ĒĢśĻ│Ā ņ׳ļŗż[2-4]. ĻĖ░Ļ│äņĀü ņåÉņāüņŚÉ ņØśĒĢ£ ņŗĀĻ▓Įļ¦Éļŗ©ņŚÉ ļīĆĒĢ£ ņ×ÉĻĘ╣ņØ┤ļéś ņåÉņāüņØĆ ņ”ēĻ░üņĀüņØĖ ņŗĀĻ▓ĮĒÄ®Ēŗ░ļō£ņØś ņ£Āļ”¼ļź╝ ņØ╝ņ£╝ĒéżĻ▓ī ļÉśĻ│Ā ņØ┤ļŖö ņŚ╝ņ”ØņØś ņ£Āļ░£Ļ│╝ ņĪ░ņĀłņØä ņØ╝ņ£╝ĒéżĻ▓ī ļÉśņ¢┤ ņŗĀĻ▓Įņä▒ņŚ╝ņ”ØņØ┤ļØ╝Ļ│Ā ļČłļ”¼ļŖö ņØ╝ļĀ©ņØś Ļ│╝ņĀĢņØ┤ ņØ╝ņ¢┤ļéśĻ▓ī ļÉ£ļŗż[2,3]. ņŗĀĻ▓Įņä▒ņŚ╝ņ”ØņØĆ ļŖÉļ”░ ņĀäļÅäņåŹļÅäļź╝ Ļ░Ćņ¦ĆĻ│Ā ņ׳ļŖö Ļ░ĆļŖö ņŗĀĻ▓Įņä¼ņ£Ā(unmyelinated C-fibersņÖĆ finely myelinated A-fibers, A╬┤ fibers)ņŚÉ ņØśĒĢśņŚ¼ ņŻ╝ļĪ£ ņ£Āļ░£ļÉśļŖöļŹ░, ņØ┤ļ¤¼ĒĢ£ ņŗĀĻ▓ĮļōżņØĆ ļłł Ēæ£ļ®┤ņŚÉ ņ╣śļ░ĆĒĢśĻ▓ī ļČäĒżĒĢśĻ│Ā ņ׳ļŗż[2,15]. ņØ┤ļĀćĻ▓ī ļČäļ╣äļÉśļŖö ņ×æņØĆ ļČäņ×ÉņØś ĒÄ®Ēŗ░ļō£ņØĖ ņŗĀĻ▓ĮĒÄ®Ēŗ░ļō£ļŖö ņŗĀĻ▓ĮĻ│äņÖĆ ļ®┤ņŚŁĻ│äņØś ņāüĒśĖņ×æņÜ®ņŚÉņä£ ņżæņÜöĒĢ£ ņŚŁĒĢĀņØä ļŗ┤ļŗ╣ĒĢśĻ▓ī ļÉ£ļŗż[2,5]. ņŗĀĻ▓Įņä▒ņŚ╝ņ”ØņØĆ ņāüņ▓ś ĒÜīļ│ĄĻ│╝ Ļ░ÉņŚ╝ņ£╝ļĪ£ļČĆĒä░ņØś ļ│┤ĒśĖļź╝ ņ£äĒĢśņŚ¼ ņ£Āļ░£ņØ┤ ļÉśĻ│Ā ņŗżņĀ£ļĪ£ ņżæņÜöĒĢ£ ņŚŁĒĢĀņØä ĒĢśņ¦Ćļ¦ī[1,16], ĻĘĖ ļČĆņ×æņÜ®ņ£╝ļĪ£ ņĢīļĀłļź┤ĻĖ░ļ│æ, ņĢäĒåĀĒö╝Ēö╝ļČĆņŚ╝, Ļ▒┤ņäĀ(psoriasis), ņŻ╝ņé¼(rosacea), ņä¼ņ£ĀĻĘ╝ĒåĄ(fibromyalgia), ņŚ╝ņ”Øņä▒ņן ņ¦łĒÖś(inflammatory bowel diseases), ņ×ÉĻ░Ćļ®┤ņŚŁņןņŚ╝(autoimmune enteritis), ņÖĖņé¼ņä▒ļćīņåÉņāü(traumatic brain injury), ĒåĄņ”Ø, ĒÄĖļæÉĒåĄ ļō▒ ņØ╝ļČĆ ņ¦łĒÖśņŚÉņä£ļŖö ļ░£ļ│æĻĖ░ņĀäņ£╝ļĪ£ļÅä ņ×æņÜ®ĒĢĀ ņłś ņ׳ņØīņØ┤ ļ│┤Ļ│ĀļÉśĻ│Ā ņ׳ļŗż[5-10].
ņÖĖļČĆņØś ņ×ÉĻĘ╣ņŚÉ ļ░śņØæĒĢśņŚ¼ ļ░£ņāØĒĢśļŖö ļ®┤ņŚŁ ļ░śņØæņØś ņ£Āļ░£Ļ│╝ ņĪ░ņĀłņŚÉ Ļ┤ĆņŚ¼ĒĢśļŖö Ļ▓āņ£╝ļĪ£ ņĢīļĀżņ¦ä ļīĆĒæ£ņĀüņØĖ ņŗĀĻ▓ĮĒÄ®Ēŗ░ļō£ļĪ£ļŖö substance P (SP), calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP), vasoactive intestinal peptide (VIP), neuropeptide Y (NPY)ļź╝ ļōż ņłś ņ׳ļŗż[17-22].
SPļŖö 11Ļ░£ņØś ņĢäļ»ĖļģĖņé░ņ£╝ļĪ£ ņØ┤ļŻ©ņ¢┤ņ¦ä tachykinin familyņØś ņŗĀĻ▓ĮĒÄ®Ēŗ░ļō£ļĪ£ ņŻ╝ļĪ£ ņŗĀĻ▓ĮņäĖĒżņÖĆ ņŚ╝ņ”ØņäĖĒżņŚÉņä£ ļČäļ╣äļÉ£ļŗż[23,24]. SPļŖö neurokinin-1 receptor (NK1R), NK2R, NK3RņØś 3Ļ░Ćņ¦Ć tachykinin ņłśņÜ®ņ▓┤ņŚÉ Ļ▓░ĒĢ®ĒĢśņŚ¼ ņ×æņÜ®ĒĢśĻ▓ī ļÉśļŖöļŹ░[25], ĒŖ╣Ē׳ NK1RņŚÉ ļåÆņØĆ ņ╣£ĒÖöļÅäļĪ£ Ļ▓░ĒĢ®ĒĢśņŚ¼ ņŚ¼ļ¤¼ Ļ░Ćņ¦Ć ņāØļ”¼ņĀü, ļ│æļ”¼ņĀü ĒÖ£ļÅÖņØä ņØ╝ņ£╝ĒéżĻ▓ī ļÉ£ļŗż[26-28]. CGRPļŖö 37Ļ░£ņØś ņĢäļ»ĖļģĖņé░ņ£╝ļĪ£ ņØ┤ļŻ©ņ¢┤ņ¦ä ļŗżĻĖ░ļŖź ņŗĀĻ▓ĮĒÄ®Ēŗ░ļō£ļĪ£, ņłśņÜ®ņ▓┤ļĪ£ļŖö calcitonin receptor-like receptor (CLR), receptor activity-modifying protein 1 (RAMP1), receptor component protein (RCP)ņØ┤ ņĢīļĀżņĀĖ ņ׳ļŗż[29,30]. ņĀäĒåĄņĀüņ£╝ļĪ£ CGRP ņłśņÜ®ņ▓┤ļŖö CGRP1Ļ│╝ CGRP2ļĪ£ ļéśļēśĻ│Ā ņä£ļĪ£ ļŗżļźĖ ļ»╝Ļ░ÉļÅäļź╝ ļ│┤ņØ┤ļŖöļŹ░, ņĪ░ņ¦üņŚÉ ļö░ļØ╝ņä£ ņ╣£ĒÖöļÅäĻ░Ć ļŗżļź┤ĻĖ░ ļĢīļ¼ĖņŚÉ ļŗżņ¢æĒĢ£ ļ░śņØæņØä ļ│┤ņØ┤ļŖö Ļ▓āņ£╝ļĪ£ ņĢīļĀżņĀĖ ņ׳ļŗż[31]. VIPļŖö ņĀäĻĄ¼ļ¼╝ņ¦łļĪ£ļČĆĒä░ 28Ļ░£ņØś ņĢäļ»ĖļģĖņé░ņ£╝ļĪ£ ņØ┤ļŻ©ņ¢┤ņ¦ä ĒÖ£ņä▒ĒśĢņ£╝ļĪ£ ĒĢ®ņä▒ļÉśļ®░[32,33], ņŻ╝ļĪ£ ņżæņČöņŗĀĻ▓ĮĻ│äņŚÉņä£ ņ£ĀļלĒĢ£ ļČĆĻĄÉĻ░ÉņŗĀĻ▓Į ļ¦Éļŗ©ņŚÉ ļ░£ĒśäļÉ£ļŗż. VIPņÖĆ pituitary adenylate cyclase-activating polypeptide (PACAP)ļŖö ļæÉ Ļ░Ćņ¦ĆņØś ņŚ░Ļ┤Ćņä▒ņØ┤ ļåÆņØĆ ņŗĀĻ▓ĮĒÄ®Ēŗ░ļō£ļĪ£, VIP/PACAP receptor 1 (VPAC1R), VPAC2R, PACAP receptor 1 (PAC1R) ņäĖ Ļ░Ćņ¦Ć ņłśņÜ®ņ▓┤ņŚÉ ņä£ļĪ£ ļŗżļźĖ ņ╣£ĒÖöļÅäļĪ£ Ļ▓░ĒĢ®ĒĢ£ļŗż[30,34,35]. NPYļŖö 36Ļ░£ņØś ņĢäļ»ĖļģĖņé░ņ£╝ļĪ£ ņØ┤ļŻ©ņ¢┤ņĪīņ£╝ļ®░ ĻĄÉĻ░ÉņŗĀĻ▓Į ļ¦Éļŗ©ņŚÉ ņŻ╝ļĪ£ ļČäĒżĒĢ£ļŗż[36-38]. NPYņłśņÜ®ņ▓┤ļŖö ŌĆ£YŌĆØņłśņÜ®ņ▓┤(Y1, Y2, Y3, Y4, Y5, Y6)ļĪ£ ļČłļ”¼Ļ│Ā, Ēżņ£ĀļÅÖļ¼╝ņŚÉņä£ļŖö 5Ļ░Ćņ¦Ć(Y1, Y2, Y4, Y5, Y6), ņé¼ļ×īņŚÉņä£ļŖö 4Ļ░Ćņ¦Ć(hY1, hY2, hY4, hY5)ļ¦ī ĻĖ░ļŖźĒĢśļŖö Ļ▓āņ£╝ļĪ£ ļ│┤Ļ│ĀļÉśĻ│Ā ņ׳ļŗż[30,39].
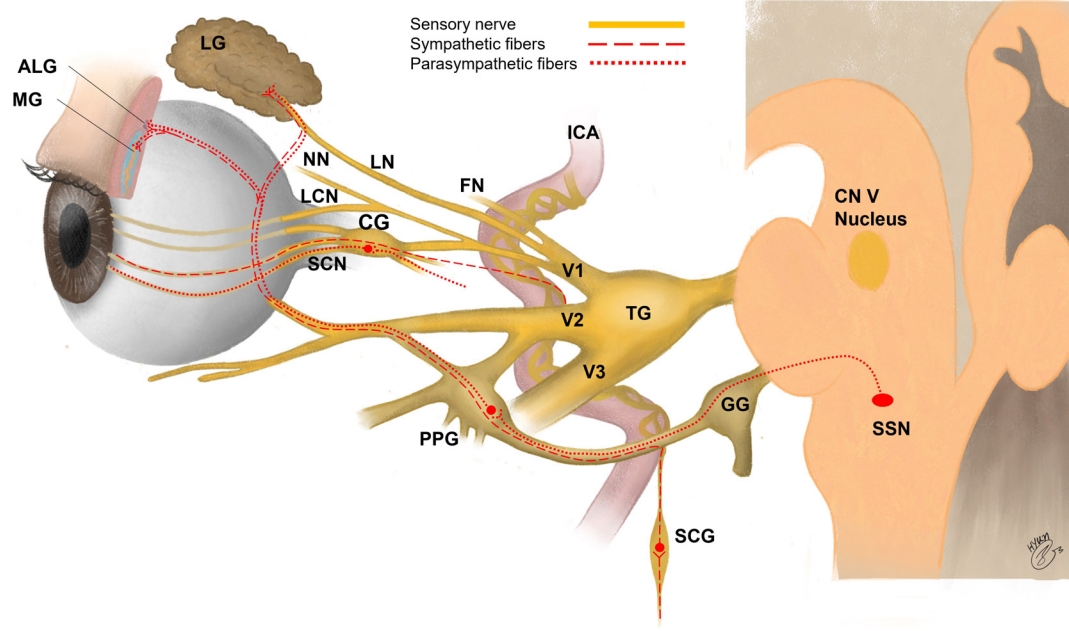
ļłł Ēæ£ļ®┤ņØĆ Ļ░üļ¦ē, Ļ▓░ļ¦ē, ļłłļ¼╝ņāś, ļ¦łņØ┤ļ┤äņāś, ļłłļ¼╝ļĪ£ ĻĄ¼ņä▒ļÉśļŖö ĻĖ░ļŖźņĀü ļŗ©ņ£äļĪ£ ņé╝ņ░©ņŗĀĻ▓ĮņØś ņĢłļČäņ¦ĆņŚÉņä£ ĻĖ░ņøÉĒĢ£ Ļ░ÉĻ░üņŗĀĻ▓Į, ņ£äļ¬®ņŗĀĻ▓ĮņĀł(superior cervical ganglion)ņŚÉņä£ ĻĖ░ņøÉĒĢ£ ĻĄÉĻ░ÉņŗĀĻ▓Į, ļéĀĻ░£ņ×ģņ▓£ņןņŗĀĻ▓ĮņĀł(pterygopalatine ganglion)ņŚÉņä£ ĻĖ░ņøÉĒĢ£ ļČĆĻĄÉĻ░ÉņŗĀĻ▓ĮņØ┤ ļČäĒżļÉ£ļŗż(Fig. 1) [40-42]. SP, CGRP, NPY, VIPņÖĆ Ļ░ÖņØĆ ņŗĀĻ▓ĮĒÄ®Ēŗ░ļō£ņÖĆ ĻĘĖ ņłśņÜ®ņ▓┤ļÅä ļłł Ēæ£ļ®┤ņØś ņŗĀĻ▓Įņä¼ņ£ĀņÖĆ ļ®┤ņŚŁņäĖĒżņŚÉ ļČäĒżĒĢśļŖöļŹ░[3,43,44], ņØ┤ļŖö ņĀĆņ×ÉļōżņØś ņØ┤ņĀä ļģ╝ļ¼ĖņŚÉ ņל ņĀĢļ”¼ļÉśņ¢┤ ņ׳ļŗż[45].
ņĄ£ĻĘ╝ņŚÉ ļÅÖļ¼╝ņŗżĒŚśņØä ņØ┤ņÜ®ĒĢ£ ļ¬ćļ¬ć ņŚ░ĻĄ¼ļź╝ ĒåĄĒĢśņŚ¼ ņĢłĻĄ¼Ļ▒┤ņĪ░ņ”ØņØś ļ░£ļ│æĻĖ░ņĀäņŚÉņä£ ņŗĀĻ▓ĮĒÄ®Ēŗ░ļō£ņÖĆ ĻĘĖ ņłśņÜ®ņ▓┤ņØś ņŚŁĒĢĀņØ┤ ļ│┤Ļ│ĀļÉśĻ│Ā ņ׳ļŗż. Ļ▒┤ņĪ░ ņŖżĒŖĖļĀłņŖżļź╝ ņØ┤ņÜ®ĒĢ£ Ļ▒┤ņä▒ņĢłņ£ĀļÅäņ▒öļ▓ä(controlled-environment chamber) ņĢłĻĄ¼Ļ▒┤ņĪ░ņ”Ø ļÅÖļ¼╝ļ¬©ļŹĖņŚÉņä£ Ļ░üļ¦ē, Ļ▓░ļ¦ē, ņé╝ņ░©ņŗĀĻ▓ĮņĀłņŚÉ SPĻ░Ć ņ”ØĻ░ĆĒĢ©Ļ│╝ SPņØś ņŻ╝ņÜö ņłśņÜ®ņ▓┤ņØĖ NK1RņØä ĻĖĖĒĢŁĒĢ©ņ£╝ļĪ£ņŹ© Ļ▒┤ņĪ░ ņŖżĒŖĖļĀłņŖżņŚÉ ņØśĒĢśņŚ¼ ņ£ĀļÅäļÉ£ ņĢłĻĄ¼Ļ▒┤ņĪ░ņ”ØņØś ņ×äņāü ņåīĻ▓¼ņØ┤ ņÖäĒÖöļÉ©ņØ┤ ļ│┤Ļ│ĀļÉśņŚłļŗż[46-49]. Ļ▒┤ņĪ░ ņŖżĒŖĖļĀłņŖżņŚÉ ņØśĒĢśņŚ¼ ņ”ØĻ░ĆļÉ£ SPĻ░Ć ļ»Ėņä▒ņłÖ ņāüĒā£ņØś ĒĢŁņøÉņĀ£ņŗ£ņäĖĒż(antigen presenting cell)ļź╝ ņä▒ņłÖņŗ£ĒéżĻ│Ā, ņĢłĻĄ¼Ļ▒┤ņĪ░ņ”Ø ļ░£ļ│æņŚÉ ņżæņÜöĒĢ£ ņ×æļÅÖņäĖĒżļĪ£ ņĄ£ĻĘ╝ņŚÉ Ļ░üĻ┤æņØä ļ░øĻ│Ā ņ׳ļŖö type 17 helper T (Th17)ņäĖĒżļĪ£ņØś ļČäĒÖöļź╝ ņ£ĀļÅäĒĢśļŖö Ļ▓āĻ│╝ ņØ┤ļ¤¼ĒĢ£ ļ│ĆĒÖöĻ░Ć NK1RņØä ĻĖĖĒĢŁĒĢ©ņ£╝ļĪ£ņŹ© ņ¢ĄņĀ£ļÉĀ ņłś ņ׳ņØīņØ┤ Yu et al [46]ņŚÉ ņØśĒĢśņŚ¼ ļ│┤Ļ│ĀļÉśņŚłļŗż. ļśÉĒĢ£, ļ░░ņłśļ”╝ĒöäņĀł(draining lymph node)ņŚÉņä£ Th17ņäĖĒżņØś ņ£ĀļÅäļź╝ ņ¢ĄņĀ£ĒĢśļŖö Ļ▓āņ£╝ļĪ£ ņĢīļĀżņ¦ä ņĪ░ņĀłTņäĖĒż(regulatory T cell, Treg)ņØś ļ╣łļÅäņÖĆ ĻĖ░ļŖźņØ┤ SPņŚÉ ņØśĒĢśņŚ¼ Ļ░ÉņåīĒĢśĻ│Ā, ļ¦łņ░¼Ļ░Ćņ¦ĆļĪ£ NK1RņØä ĻĖĖĒĢŁĒĢ©ņ£╝ļĪ£ņŹ© TregņØś ņĪ░ņĀłĻĖ░ļŖźņØä ļ│ĄņøÉņŗ£Ēé¼ ņłś ņ׳ņØīņØ┤ ļ│┤Ļ│ĀļÉśņŚłļŗż[48]. ņĢłĻĄ¼Ļ▒┤ņĪ░ņ”Ø ļ®┤ņŚŁĒĢÖņĀü ļ░£ļ│æĻĖ░ņĀäņŚÉņä£ ņżæņÜöĒĢ£ ņŚŁĒĢĀņØä ĒĢĀ Ļ▓āņ£╝ļĪ£ ņāØĻ░üļÉśļŖö Ļ░üļ¦ē ļ”╝ĒöäĻ┤Ć ņŗĀņāØņŚÉļÅä SP/NK1R systemņØ┤ Ļ┤ĆņŚ¼ĒĢ©ņØ┤ ņ”Øļ¬ģļÉśņŚłĻ│Ā, ĒŖ╣Ē׳ ļ”╝ĒöäĻ┤ĆņäĖĒżņŚÉņä£ vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 3 (VEGFR3)ņØś ļ░£Ēśä ņ”ØĻ░Ćļź╝ ĒåĄĒĢśņŚ¼ SPĻ░Ć ļ”╝ĒöäĻ┤Ć ņŗĀņāØņŚÉ Ļ┤ĆņŚ¼ĒĢ©ņØ┤ ļ”╝ĒöäĻ┤ĆņäĖĒżļ░░ņ¢æņØä ĒåĄĒĢśņŚ¼ ņ”Øļ¬ģļÉśņŚłļŗż[49]. ĒĢśņ¦Ćļ¦ī SPĻ░Ć ņé╝Ēł¼ņĢĢ ņŖżĒŖĖļĀłņŖżņŚÉ ņØśĒĢ£ Ļ░üļ¦ēņāüĒö╝ņäĖĒżņØś ņäĖĒżņ×Éļ®Ėņé¼(apoptosis)ņŚÉ ļīĆĒĢ£ ļ│┤ĒśĖ ĒÜ©Ļ│╝ļź╝ Ļ░¢Ļ│Ā[50], ņ¦üņĀæņĀüņ£╝ļĪ£ ņĪ░ņ¦üņ×¼ņāØņØä ļÅĢļŖö M2ĒśĢņØś Ēü░ĒżņŗØņäĖĒż(macrophages)ļź╝ ņ£ĀļÅäĒĢ£ļŗżļŖö ļ│┤Ļ│ĀļÅä ņ׳ņ¢┤[51], ņĢłĻĄ¼Ļ▒┤ņĪ░ņ”Ø, ĻĘĖņŚÉ ļö░ļźĖ ņĪ░ņ¦üņåÉņāüņØś ļŗ©Ļ│äņŚÉ ļö░ļØ╝ņä£ SPņØś ņŚŁĒĢĀņØ┤ ļŗżļź╝ Ļ░ĆļŖźņä▒ņØä Ļ│ĀļĀżĒĢ┤ ļ│╝ ĒĢäņÜöĻ░Ć ņ׳Ļ│Ā ņČöĻ░ĆņĀüņØĖ ņŚ░ĻĄ¼Ļ░Ć ĒĢäņÜöĒĢśļŗż.
ņĢłĻĄ¼Ļ▒┤ņĪ░ņ”Ø ĒÖśņ×ÉņØś ļłł Ēæ£ļ®┤ņŚÉņä£ ņŚ╝ņ”Øņä▒ ņŗ£ĒåĀņ╣┤ņØĖ(proinflammatory cytokines)ņØś ļåŹļÅä ņ”ØĻ░ĆĻ░Ć ļ│┤Ļ│ĀļÉśĻ│Ā, ņć╝ĻĘĖļĀīņ”ØĒøäĻĄ░ ĒÖśņ×ÉņØś ņ╣©ņŚÉņä£ ļē┤ļĪ£ĒÄ®Ēŗ░ļō£ ļåŹļÅäņØś ļ│ĆĒÖöĻ░Ć Ļ┤Ćņ░░ļÉśļ®┤ņä£, ņŗĀĻ▓Įņä▒ņŚ╝ņ”ØņØ┤ ņĢłĻĄ¼Ļ▒┤ņĪ░ņ”ØņØś ļ░£ļ│æņŚÉļÅä ņżæņÜöĒĢ£ ņŚŁĒĢĀņØä ĒĢĀ Ļ▓āņ£╝ļĪ£ ĻĖ░ļīĆĻ░Ć ļÉśņŚłņ£╝ļéś ņŗżņĀ£ļĪ£ ņĢłĻĄ¼Ļ▒┤ņĪ░ņ”Ø ĒÖśņ×ÉņØś ļłłļ¼╝ņŚÉņä£ ļē┤ļĪ£ĒÄ®Ēŗ░ļō£ņØś ļ│ĆĒÖöļź╝ ļ│┤Ļ│ĀĒĢ£ ņŚ░ĻĄ¼ļŖö ļ¦żņÜ░ ņĀ£ĒĢ£ņĀüņØ┤ļŗż[52-56]. Lambiase et al [57]ņØĆ 19ļ¬ģņØś ņĢłĻĄ¼Ļ▒┤ņĪ░ņ”Ø ĒÖśņ×É(ņć╝ĻĘĖļĀī 5ļ¬ģ, ļ╣äņć╝ĻĘĖļĀī 10ļ¬ģ, ņĢłņ▓£Ēżņ░Į 4ļ¬ģ)ņÖĆ ļīĆņĪ░ĻĄ░ 12ļ¬ģņØś ļłłļ¼╝ņŚÉņä£ ļē┤ļĪ£ĒÄ®Ēŗ░ļō£ ļåŹļÅäļź╝ ļČäņäØĒĢśņŚ¼ ņĢłĻĄ¼Ļ▒┤ņĪ░ņ”Ø ĒÖśņ×ÉņŚÉņä£ CGRPņÖĆ NPY ļåŹļÅäĻ░Ć Ļ░ÉņåīĒĢśĻ│Ā ņŗĀĻ▓Įņä▒ņןņØĖņ×É(nerve growth factor)ņØś ļåŹļÅäĻ░Ć ņ”ØĻ░ĆļÉśņŚłņØīņØä ļ│┤Ļ│ĀĒĢśņśĆļŗż. ņØ┤ ņŚ░ĻĄ¼ņŚÉņä£ļŖö SPņÖĆ VIP ļåŹļÅäļŖö ļ│ĆĒĢśņ¦Ć ņĢŖņĢśļŖöļŹ░, ĒŖ╣Ē׳ SP ļåŹļÅäļŖö ņć╝ĻĘĖļĀī, ļ╣äņć╝ĻĘĖļĀī ļ¬©ļæÉņŚÉņä£ ņ”ØĻ░ĆĒĢśņ¦Ć ņĢŖņĢä ĻĖ░ņĪ┤ņØś ļÅÖļ¼╝ņŗżĒŚś Ļ▓░Ļ│╝ļōżĻ│╝ ļŗżļźĖ Ļ▓░Ļ│╝ļź╝ ļ│┤ņŚ¼ņŻ╝ņŚłļŗż. ņØ┤ņŚÉ ļīĆĒĢ£ ĒĢ┤ņäØņØĆ ņŻ╝ņØśĻ░Ć ĒĢäņÜöĒĢ£ļŹ░, ņŚ╝ņ”Øņä▒ ņŗ£ĒåĀņ╣┤ņØĖņØ┤ļ®┤ņä£ ņĢłĻĄ¼Ļ▒┤ņĪ░ņ”ØņŚÉņä£ ņ”ØĻ░ĆĒĢśļŖö Ļ▓āņ£╝ļĪ£ ņĢīļĀżņ¦ä interleukin-6ņØś ļłłļ¼╝ļé┤ ļåŹļÅä ņ”ØĻ░ĆĻ░Ć Ļ░üļ¦ē ĻĖ░ņĀĆņŗĀĻ▓Įņ¢╝ĻĖ░(subbasal nerve plexus)ņØś ņŗĀĻ▓Įņä¼ņ£Ā ļæÉĻ╗śļź╝ Ļ░Éņåīņŗ£ņ╝░ļŗżļŖö ļ│┤Ļ│ĀĒĢśņśĆĻ│Ā[58,59], Ļ░üļ¦ē Ļ░ÉĻ░üņĀĆĒĢś(corneal hypesthesia) ļśÉļŖö ļŗ╣ļć©ņä▒ ļ¦Éņ┤łņŗĀĻ▓Įļ│æņ”Ø(diabetic peripheral neuropathy) ņāüĒā£ņŚÉņä£ ļłłļ¼╝ņØś SPĻ░Ć Ļ░ÉņåīĒĢśņśĆļŗżļŖö ļ│┤Ļ│Āļź╝ ņóģĒĢ®ņĀüņ£╝ļĪ£ Ļ│ĀļĀżĒĢĀ ļĢī[60-62], ņĢłĻĄ¼Ļ▒┤ņĪ░ņ”ØņØ┤ ņ¦äĒ¢ēļÉśļ®┤ņä£ ļ░£ņāØĒĢ£ Ļ░üļ¦ēņŗĀĻ▓ĮņØś Ļ░ÉņåīĻ░Ć ņ”ØĻ░ĆļÉ£ SP ļČäļ╣äļź╝ ņāüņćäņŗ£ņ╝░ņØä Ļ░ĆļŖźņä▒ņØä Ļ│ĀļĀżĒĢ┤ļ│╝ ņłś ņ׳Ļ│Ā ņØ┤ņŚÉ ļīĆĒĢ┤ņä£ļŖö ņČöĻ░Ć ņŚ░ĻĄ¼Ļ░Ć ĒĢäņÜöĒĢśļŗż.
ņĢ×ņä£ ņé┤ĒÄ┤ļ│Ė ļ░öņÖĆ Ļ░ÖņØ┤ ļÅÖļ¼╝ņŗżĒŚśņØä ĒåĄĒĢ£ ņĢłĻĄ¼Ļ▒┤ņĪ░ņ”ØņØś ļ░£ļ│æĻĖ░ņĀäņŚÉ ļīĆĒĢ£ ņŚ░ĻĄ¼ņŚÉņä£ņÖĆ ļŗ¼ļ”¼ ņŗżņĀ£ ņĢłĻĄ¼Ļ▒┤ņĪ░ņ”Ø ĒÖśņ×Éļź╝ ļīĆņāüņ£╝ļĪ£ ĒĢ£ ņ×äņāü ņŚ░ĻĄ¼ņŚÉņä£ SPņØś ļ│ĆĒÖöņÖĆ ņŚŁĒĢĀņØĆ ņĢäņ¦ü ļ░ØĒśĆņ¦Ćņ¦Ć ņĢŖņĢśļŗż. ĒĢśņ¦Ćļ¦ī ņØśņØĖņä▒ ņĢłĻĄ¼Ļ▒┤ņĪ░ņ”ØĻ│╝ Ļ┤ĆļĀ©ĒĢśņŚ¼ņä£ļŖö SPĻ░Ć ņ×äņāüņĀüņ£╝ļĪ£ ņØśļ»Ė ņ׳ļŖö ļ│ĆĒÖöļź╝ ļ│┤ņØ┤Ļ│Ā, ļ░£ļ│æĻĖ░ņĀäĻ│╝ Ļ┤ĆļĀ©ņØ┤ ņ׳ņØä Ļ░ĆļŖźņä▒ņØä ņ£ĀņČöĒĢĀ ņłś ņ׳ļŖö Ļ▓░Ļ│╝ļōżņØ┤ ņóĆ ļŹö ļ░£Ļ▓¼ļÉ£ļŗż.
ĻĄ┤ņĀłņłśņłĀ ĒøäņŚÉļŖö ļłłļ¼╝ ņāØņä▒, ļłłļ¼╝ņØś ņ¦ł, ļłłĻ╣£ļ╣Īņ×ä ļ░śņé¼ņØś Ļ░ÉņåīļĪ£ ņØĖĒĢśņŚ¼ ņĢłĻĄ¼Ļ▒┤ņĪ░ņ”ØņØ┤ ļ░£ņāØĒĢśļŖö Ļ▓āņØ┤ ņĢīļĀżņĀĖ ņ׳Ļ│Ā[63], ļØ╝ņŗØ(laser-assisted in situ keratomileusis, LASIK)ņØ┤ļéś ĻĄ┤ņĀłĻĄÉņĀĢļĀłņØ┤ņĀĆĻ░üļ¦ēņĀłņĀ£ņłĀ(photorefractive keratectomy, PRK) ĒøäņŚÉ ļłłļ¼╝ ļé┤ ņŗĀĻ▓ĮĒÄ®Ēŗ░ļō£ņØś ļåŹļÅäĻ░Ć ļ│ĆĒÖöļÉ©ņØ┤ ļ│┤Ļ│ĀļÉśĻ│Ā ņ׳ļŗż[63-67]. ļØ╝ņŗØņłśņłĀ Ēøä ļłłļ¼╝ņØś SP ļåŹļÅäļŖö 3Ļ░£ņøöĻ╣īņ¦Ć ņ”ØĻ░ĆļÉ©ņØ┤ ļ│┤Ļ│ĀļÉśņŚłņ¦Ćļ¦ī[65,66], 12Ļ░£ņøöņ¦ĖņŚÉļŖö ļīĆņĪ░ĻĄ░Ļ│╝ ņ░©ņØ┤Ļ░Ć ņŚåļŗżĻ│Ā ļ│┤Ļ│ĀļÉśņŚłļŗż[67]. ļØ╝ņŗØņłśņłĀ ĒøäņŚÉļŖö ļłłļ¼╝ņØś SP ļåŹļÅäĻ░Ć Ļ░üļ¦ēņŗĀĻ▓Įņä¼ņ£Ā ļ░ĆļÅäņÖĆ ļ░śļ╣äļĪĆĒĢ┤ņä£, ņŗĀĻ▓Įļ░ĆļÅäĻ░Ć ļåÆņØä ļĢī ļłłļ¼╝ ļé┤ SP ļåŹļÅäĻ░Ć ļé«ņĢśļŗżĻ│Ā ļ│┤Ļ│ĀļÉśņŚłļŗż[65]. ļØ╝ņŗØņłśņłĀ Ēøä ļłłļ¼╝ņØś CGRP ļåŹļÅäņŚÉ ļīĆĒĢ£ Ļ▓░Ļ│╝ļŖö SPņÖĆļŖö ļ░śļīĆļĪ£ ņĀäĒ¢źņĀüņØĖ ņČöņĀü ņŚ░ĻĄ¼ņŚÉņä£ļŖö 3Ļ░£ņøöĻ╣īņ¦Ć ļ│ĆĒÖöĻ░Ć ņŚåņŚłļŗżĻ│Ā ļ│┤Ļ│ĀļÉśĻ│Ā ņ׳Ļ│Ā[66], ņłśņłĀ Ēøä 12Ļ░£ņøöņ¦ĖņŚÉ ņŗ£Ē¢ēĒĢ£ ļŗ©ļ®┤ ņŚ░ĻĄ¼(cross-sectional study)ņŚÉņä£ļŖö ņĀĢņāüļīĆņĪ░ĻĄ░ņŚÉ ļ╣äĒĢ┤ņä£ ņ£ĀņØśĒĢśĻ▓ī ļåÆņĢśļŗżĻ│Ā ļ│┤Ļ│ĀļÉśņŚłļŗż[67]. PRK ņłśņłĀ ņĀäĻ│╝ ļ╣äĻĄÉĒĢ£ ņĀäĒ¢źņĀüņØĖ ņŚ░ĻĄ¼ņŚÉņä£ ļłłļ¼╝ņØś CGRP ļåŹļÅäļŖö PRK Ēøä 2ņØ╝Ļ╣īņ¦Ć ņ”ØĻ░ĆĒĢśņŚ¼ ņĄ£ļīĆņ╣śņŚÉ ļÅäļŗ¼ĒĢ£ Ēøä 7ņØ╝ņ¦ĖĻ╣īņ¦Ć Ļ░ÉņåīĒĢ©ņØ┤ ļ│┤Ļ│ĀļÉśņŚłļŗż[64]. ņ▓śņØī ņØ┤ĒŗĆĻ░ä ņ”ØĻ░ĆĒĢ£ CGRPļŖö ņåÉņāüļÉ£ Ļ░üļ¦ēņŗĀĻ▓Įņ£╝ļĪ£ļČĆĒä░ ņ£Āļ”¼ļÉ£ Ļ▓āņ£╝ļĪ£ ņāØĻ░üļÉśļŖöļŹ░, ņłśņłĀ ņ¦üĒøäņØś ļłłļ¼╝ ļČäļ╣ä ņ”ØĻ░ĆņŚÉļÅä ļČłĻĄ¼ĒĢśĻ│Ā ļåŹļÅäĻ░Ć Ļ░ÉņåīĒĢśņ¦Ć ņĢŖņĢäņä£ ņāüļŗ╣ļ¤ēņØś CGRPĻ░Ć ņåÉņāüļÉ£ ņŗĀĻ▓Įņ£╝ļĪ£ļČĆĒä░ ņ£Āļ”¼ļÉśņŚłņØīņØä ņ£ĀņČöĒĢĀ ņłś ņ׳ļŗż[64]. ņĀĢļ”¼ĒĢśņ×Éļ®┤, ĻĄ┤ņĀłņłśņłĀ ĒøäņŚÉļŖö ļłłļ¼╝ņØś SPņÖĆ CGRP ļåŹļÅäņØś ļ│ĆĒÖöĻ░Ć ļ│┤Ļ│ĀļÉśĻ│Ā ņ׳ņ£╝ļ®░, ņØ┤ļŖö ĻĄ┤ņĀłņłśņłĀņŚÉ ņØśĒĢ£ Ļ░üļ¦ēņŗĀĻ▓ĮņåÉņāüĻ│╝ ņŚ░Ļ┤ĆļÉĀ Ļ░ĆļŖźņä▒ņØä ņāØĻ░üĒĢĀ ņłś ņ׳ļŗż. ĒĢśņ¦Ćļ¦ī ļ│ĆĒÖöļÉ£ ņŗĀĻ▓ĮĒÄ®Ēŗ░ļō£Ļ░Ć ņłĀ Ēøä ņĢłĻĄ¼Ļ▒┤ņĪ░ņ”ØņØś ļ░£ņāØņŚÉ ĻĖ░ņŚ¼ĒĢśļŖö ļČĆļČäņØĆ Ē¢źĒøä ņóĆ ļŹö ņŚ░ĻĄ¼Ļ░Ć ĒĢäņÜöĒĢśļŗż.
ļ░▒ļé┤ņןņłśņłĀ Ēøä ņĢłĻĄ¼Ļ▒┤ņĪ░ņ”Ø ņĢģĒÖöņŚÉ ļīĆĒĢ┤ņä£ļŖö ņĄ£ĻĘ╝ņŚÉ ņ×äņāüņĀüņ£╝ļĪ£ Ļ┤Ćņŗ¼ņØ┤ ļ¦ÄņØĆ ļČĆļČäņØ┤ļŗż. ĒĢśņ¦Ćļ¦ī ņĢäņ¦üĻ╣īņ¦Ć ļ░▒ļé┤ņןņłśņłĀ Ēøä ņĢłĻĄ¼Ļ▒┤ņĪ░ņ”Ø ļ░£ņāØĻ│╝ Ļ┤ĆļĀ©ĒĢśņŚ¼ ņŗĀĻ▓ĮĒÄ®Ēŗ░ļō£ņØś ņŚŁĒĢĀņØä ļ│┤ļŖö ņŚ░ĻĄ¼ļŖö ņĀĆņ×ÉļōżņØś Ļ▓ĆņāēņŚÉņä£ļŖö ļ░£Ļ▓¼ļÉśņ¦Ć ņĢŖņĢśļŗż. ļŗżļ¦ī ņłĀ Ēøä ņĢłĻĄ¼Ļ▒┤ņĪ░ņ”ØņØĆ ņĢäļŗłņ¦Ćļ¦ī ņłśņłĀ ņŗ£ ĒåĄņ”ØĻ│╝ Ļ┤ĆļĀ©ĒĢśņŚ¼, ļŗ╣ļć© ĒÖśņ×ÉņŚÉņä£ ņŚ░ņØ┤ņ¢┤ ņ¢æņĢł ļ░▒ļé┤ņןņłśņłĀņØä ņŗ£Ē¢ēĒĢ£(1ņØ╝ ļśÉļŖö 1ņŻ╝ Ļ░äĻ▓®) Ļ▓ĮņÜ░ ņĢłĻĄ¼ļ░®ņłśņØś SPņÖĆ monocyte chemoattractant protein 1ņØ┤ ļéśņżæņŚÉ ņłśņłĀĒĢ£ ļłłņŚÉņä£ ņ£ĀņØśĒĢśĻ▓ī ļåÆņĢäņä£, ĻĄÉĻ░Éņä▒ ņŚ╝ņ”Ø ļ░śņØæ(sympathetic inflammatory responses)ņØä ĒåĄĒĢśņŚ¼ ļéśņżæņŚÉ ņłśņłĀĒĢ£ ļłłņŚÉņä£ ļŹö ņŗ¼ĒĢ£ ĒåĄņ”ØņØä ņ£Āļ░£ĒĢĀ Ļ░ĆļŖźņä▒ņØä ļ│┤Ļ│ĀĒĢ£ ļģ╝ļ¼ĖņØ┤ ņĄ£ĻĘ╝ņŚÉ ļ░£Ēæ£ļÉśņŚłļŗż[68].
ņĮśĒāØĒŖĖļĀīņ”ł ņ░®ņÜ®ņØĆ ļłłļ¼╝ņĖĄņØś ļČłņĢłņĀĢ, ļłłļ¼╝ ņ”Øļ░£ņØś ņ”ØĻ░Ć, ļłłļ¼╝ļ¦ē ļ░śļŗ¼ļØĀ(tear film meniscus)ņØś ņĀĆĒĢś, ĻĖ░ļ│Ėļłłļ¼╝(basal tear) ĒÜīņĀäņ£© ņĀĆĒĢś, ļłłļ¼╝ ņé╝Ēł¼ņĢĢ ņ”ØĻ░Ć, ĻĖ░ļ”äņĖĄ ļ│ĆĒÖöņÖĆ ļĀīņ”ł ņŖĄņ£żņä▒ ņĀĆĒĢś, Ļ▓░ļ¦ē ņČ®ĒśłĻ│╝ ņāüĒö╝ņåÉņāü ļō▒ņØä ņ┤łļלĒĢśņŚ¼ ļłłļ¼╝ļ¦ēĻ│╝ ļłł Ēæ£ļ®┤ņØś ņāØļ”¼ņĀü ļ│ĆĒÖöļź╝ ņ┤łļלĒĢśļŖö Ļ▓āņ£╝ļĪ£ ņĢīļĀżņĀĖ ņ׳ļŗż[14,69]. ĒĢśņ¦Ćļ¦ī ņĮśĒāØĒŖĖļĀīņ”ł ņ░®ņÜ®ņŚÉ ļö░ļźĖ ļłłļ¼╝ņØś ņŗĀĻ▓ĮĒÄ®Ēŗ░ļō£ ļ│ĆĒÖöņŚÉ ļīĆĒĢ£ ņŚ░ĻĄ¼ļŖö ņĢäņ¦üĻ╣īņ¦Ć ņŚ¼ņ¦ĆĻ░Ć ļ¦Äļŗż. ņĮśĒāØĒŖĖļĀīņ”ł ņ░®ņÜ®ņ×É 20ļ¬ģĻ│╝ ļ╣äņ░®ņÜ®ņ×É 20ļ¬ģņØä ļ╣äĻĄÉĒĢ£ ņŚ░ĻĄ¼ņŚÉņä£ļŖö SPņÖĆ CGRPņØś ļåŹļÅäļŖö ņ£ĀņØśĒĢ£ ņ░©ņØ┤Ļ░Ć ņŚåņŚłĻ│Ā, ĒĢ©Ļ╗ś ļČäņäØĒĢ£ Ļ░üļ¦ēņŗĀĻ▓Į ĒśĢĒā£ņÖĆ Ļ░üļ¦ēņ¦ĆĻ░üļÅä ņ░©ņØ┤Ļ░Ć ņŚåņŚłļŗż[70]. ĒĢśņ¦Ćļ¦ī ņŗĀĻ▓ĮņØś ļ░ĆļÅäņÖĆ ļłłļ¼╝ņØś CGRP ļåŹļÅä ļ░Å Ļ░üļ¦ēņ¦ĆĻ░üņØĆ ņ£ĀņØśĒĢ£ ņāüĻ┤ĆĻ┤ĆĻ│äĻ░Ć Ļ┤Ćņ░░ļÉśņŚłļŗż. ļ░śļ®┤, ņĮśĒāØĒŖĖļĀīņ”ł ņ░®ņÜ®ņ×É ņżæ ļČłĒÄĖĻ░ÉņØä ļŖÉļü╝ļŖö 30ļ¬ģĻ│╝ ļČłĒÄĖĻ░ÉņØä ļŖÉļü╝ņ¦Ć ņĢŖļŖö 30ļ¬ģņØä ļ╣äĻĄÉĒĢśņśĆņØä ļĢīļŖö ļłłļ¼╝ņØś SPĻ░Ć ļČłĒÄĖĻ░ÉņØä ļŖÉļü╝ļŖö ĻĄ░ņŚÉņä£ ņ£ĀņØśĒĢśĻ▓ī ļåÆņĢśļŗż[69]. ņĢäņ¦ü ņŚ░ĻĄ¼ Ļ▓░Ļ│╝Ļ░Ć ļ¦Äņ¦Ć ņĢŖņĢäņä£ ĒÖĢņĀĢņĀüņ£╝ļĪ£ ļŗ©ņĀĢĒĢĀ ņłśļŖö ņŚåņ¦Ćļ¦ī, ļłłļ¼╝ ņżæ ņŗĀĻ▓ĮĒÄ®Ēŗ░ļō£ņØś ļåŹļÅä, ĒŖ╣Ē׳ SPļŖö ņĮśĒāØĒŖĖļĀīņ”ł ņ░®ņÜ® ņ×Éņ▓┤ļ│┤ļŗżļŖö ņĮśĒāØĒŖĖļĀīņ”ł ļČłĒÄĖĻ░ÉĻ│╝ ļŹö Ļ┤ĆļĀ©ņØ┤ ņ׳ņØä Ļ░ĆļŖźņä▒ņØ┤ ņ׳ņ¢┤ ņĮśĒāØĒŖĖļĀīņ”ł ļČłĒÄĖĻ░É ļśÉļŖö ņĮśĒāØĒŖĖļĀīņ”łļĪ£ ņØĖĒĢ£ ņĢłĻĄ¼Ļ▒┤ņĪ░ņ”ØĻ│╝ņØś Ļ┤ĆļĀ© Ļ░ĆļŖźņä▒ņØä ņŗ£ņé¼ĒĢ£ļŗżĻ│Ā ĒĢśĻ▓Āļŗż. ļłłļ¼╝ņØś CGRP ļåŹļÅä ņŚŁņŗ£ ņĮśĒāØĒŖĖļĀīņ”ł ņ░®ņÜ® ņ×Éņ▓┤ļ│┤ļŗżļŖö Ļ░üļ¦ēņŗĀĻ▓ĮņØś ļ░ĆļÅäņÖĆ ņóĆ ļŹö Ļ┤ĆļĀ©ļÉ£ Ļ▓āņ£╝ļĪ£ ļ│┤ņØĖļŗż.
ņØ┤ ļģ╝ļ¼ĖņŚÉņä£ļŖö ņĢłĻĄ¼Ļ▒┤ņĪ░ņ”ØņØś ļ░£ļ│æĻĖ░ņĀäĻ│╝ Ļ┤ĆļĀ©ĒĢśņŚ¼ ņŗĀĻ▓ĮĒÄ®Ēŗ░ļō£ņŚÉ ļīĆĒĢ£ ņĄ£ĻĘ╝ ņŗżĒŚśņĀü ņŚ░ĻĄ¼ Ļ▓░Ļ│╝ļōżĻ│╝ Ēśäņ×¼Ļ╣īņ¦ĆņØś ņ×äņāü ņŚ░ĻĄ¼ Ļ▓░Ļ│╝ļōż ĻĘĖļ”¼Ļ│Ā ņØśņØĖņä▒ ņĢłĻĄ¼Ļ▒┤ņĪ░ņ”ØĻ│╝ Ļ┤ĆļĀ©ĒĢśņŚ¼ ņŗĀĻ▓ĮĒÄ®Ēŗ░ļō£ņØś ļ│ĆĒÖöļź╝ ļ│Ė ņ×äņāü ņŚ░ĻĄ¼ļōżņØä Ļ░äļŗ©Ē׳ ņé┤ĒÄ┤ļ│┤ņĢśļŗż. ņĢäņ¦üĻ╣īņ¦Ć ņĢłĻĄ¼Ļ▒┤ņĪ░ņ”ØņØś ļ░£ļ│æĻĖ░ņĀäĻ│╝ Ļ┤ĆļĀ©ĒĢśņŚ¼ ņŗĀĻ▓ĮĒÄ®Ēŗ░ļō£ņØś ņŚŁĒĢĀņØĆ ļ¬ģĒÖĢĒĢśņ¦Ć ņĢŖņ¦Ćļ¦ī, ĻĖ░ņĀäņØä Ļ│ĀļĀżĒĢ£ Ļ░ĆļŖźņä▒Ļ│╝ ņĄ£ĻĘ╝ņØś ņŚ░ĻĄ¼ Ļ▓░Ļ│╝ļōżņØä ņóģĒĢ®ĒĢ┤ļ│┤ļ®┤ ņŗĀĻ▓ĮĒÄ®Ēŗ░ļō£Ļ░Ć ņĢłĻĄ¼Ļ▒┤ņĪ░ņ”Ø ļ░£ļ│æņŚÉ Ļ┤ĆņŚ¼ĒĢĀ Ļ░ĆļŖźņä▒ņØĆ ļåÆņØä Ļ▓āņ£╝ļĪ£ ņāØĻ░üļÉ£ļŗż. ĒĢśņ¦Ćļ¦ī ņŗżĒŚśņĀü ņŚ░ĻĄ¼Ļ░Ć ņŗżņĀ£ ņ×äņāü ņŚ░ĻĄ¼ Ļ▓░Ļ│╝ņÖĆ ņ░©ņØ┤ļź╝ ļ│┤ņØ┤ļŖö ļČĆļČäņØ┤ Ļ░Ćņן Ēü░ ļ¼ĖņĀ£ņĀÉņØĖļŹ░, ņØ┤ļŖö ņĢłĻĄ¼Ļ▒┤ņĪ░ņ”ØņØś ļ░£ļ│æ ņŗ£ĻĖ░ņÖĆ ņżæņ”ØļÅäņŚÉ ļö░ļØ╝ņä£ ņŗĀĻ▓ĮĒÄ®Ēŗ░ļō£ņØś ņŚŁĒĢĀņØ┤ ņāüļ░śļÉĀ ņłś ņ׳Ļ│Ā, ņĢłĻĄ¼Ļ▒┤ņĪ░ņ”Ø ņ¦äĒ¢ēņŚÉ ļö░ļźĖ Ļ░üļ¦ēņŗĀĻ▓ĮņåÉņāüņØ┤ ņ”ØĻ░ĆļÉ£ ņŗĀĻ▓ĮĒÄ®Ēŗ░ļō£ņØś ļČäļ╣äļź╝ Ļ░Ćļ”┤ ņłś ņ׳ļŖöļŹ░[71-73], ĻĖ░ņĪ┤ ņ×äņāü ņŚ░ĻĄ¼ļŖö ĻĘĖļ¤¼ĒĢ£ ļČĆļČäņØ┤ Ļ│ĀļĀżļÉśņ¦Ć ļ¬╗ĒĢ£ Ļ▓āņØ┤ ĒĢ£Ļ│äņĀÉņ£╝ļĪ£ ņāØĻ░üļÉ£ļŗż. ĻĘĖļ¤░ ņĀÉņŚÉņä£ ļ╣äĻĄÉņĀü ļ░£ļ│æ ņŗ£ĻĖ░Ļ░Ć ļ¬ģĒÖĢĒĢśĻ│Ā ņåÉņāüņØś ņĀĢļÅäĻ░Ć ņØ╝ņĀĢĒĢ£ ņØśņØĖņä▒ ņĢłĻĄ¼Ļ▒┤ņĪ░ņ”ØņØĆ ņ×äņāü ņŚ░ĻĄ¼ļź╝ ņ£äĒĢ£ ņóŗņØĆ ņĢłĻĄ¼Ļ▒┤ņĪ░ņ”Ø ļ¬©ļŹĖļĪ£ ĻĖ░ļīĆļÉ£ļŗż. ņĢäņ¦üņØĆ ļ╣łņĢĮĒĢśņ¦Ćļ¦ī Ēśäņ×¼Ļ╣īņ¦ĆņØś ņŚ░ĻĄ¼ Ļ▓░Ļ│╝ļōżņØ┤ ņ¢┤ļŖÉ ņĀĢļÅä ņØśņØĖņä▒ ņĢłĻĄ¼Ļ▒┤ņĪ░ņ”ØņØś ļ░£ļ│æņŚÉ ņŗĀĻ▓ĮĒÄ®Ēŗ░ļō£Ļ░Ć Ļ┤ĆņŚ¼ĒĢĀ Ļ░ĆļŖźņä▒ņØä ļ│┤ņŚ¼ņŻ╝Ļ│Ā ņ׳ļŗżĻ│Ā ņāØĻ░üļÉśĻ│Ā, Ļ┤ĆļĀ©ļÉ£ ņŚ░ĻĄ¼ Ļ▓░Ļ│╝ļōżņØ┤ ņóĆ ļŹö ņīōņŚ¼Ļ░Ćļ®┤ ņĢłĻĄ¼Ļ▒┤ņĪ░ņ”ØņØś ļ░£ļ│æĻĖ░ņĀäņŚÉņä£ ņŗĀĻ▓ĮĒÄ®Ēŗ░ļō£ņØś ņŚŁĒĢĀņØ┤ ņóĆ ļŹö ļ¬ģĒÖĢĒĢ┤ņ¦ł ņłś ņ׳ņØä Ļ▓āņ£╝ļĪ£ ĻĖ░ļīĆĒĢ£ļŗż.
Figure┬Ā1.
Schematic drawing for innervation of the lacrimal functional unit. Modified from Hwang et al[45]. ALG = accessory lacrimal glands; MG = meibomian gland; LG = lacrimal gland; NN = nasociliary nerve; LCN = long ciliary nerve; SCN = short ciliary nerve; LN = lacrimal nerve; CG = ciliary ganglion; FN = frontal nerve; PPG = pterygopalatine (sphenopalatine) ganglion; ICA = internal carotid artery; TG = trigeminal ganglion; SCG = superior cervical ganglion; GG = geniculate ganglion; CN = cranial nerve; SSN = superior salivatory nucleus.
REFERENCES
1) Chiu IM, von Hehn CA, Woolf CJ. Neurogenic inflammation and the peripheral nervous system in host defense and immunopathology. Nat Neurosci 2012;15:1063-7.



2) Beuerman RW, Stern ME. Neurogenic inflammation: a first line of defense for the ocular surface. Ocul Surf 2005;3:S203-6.


3) Sabatino F, Di Zazzo A, De Simone L, Bonini S. The intriguing role of neuropeptides at the ocular surface. Ocul Surf 2017;15:2-14.


4) Mashaghi A, Marmalidou A, Tehrani M, et al. Neuropeptide substance P and the immune response. Cell Mol Life Sci 2016;73:4249-64.



5) Mantelli F, Micera A, Sacchetti M, Bonini S. Neurogenic inflammation of the ocular surface. Curr Opin Allergy Clin Immunol 2010;10:498-504.


6) Corrigan F, Mander KA, Leonard AV, Vink R. Neurogenic inflammation after traumatic brain injury and its potentiation of classical inflammation. J Neuroinflammation 2016;13:264.



8) Littlejohn G, Guymer E. Neurogenic inflammation in fibromyalgia. Semin Immunopathol 2018;40:291-300.


9) Ramachandran R. Neurogenic inflammation and its role in migraine. Semin Immunopathol 2018;40:301-14.


10) Matsuda M, Huh Y, Ji RR. Roles of inflammation, neurogenic inflammation, and neuroinflammation in pain. J Anesth 2019;33:131-9.


11) The definition and classification of dry eye disease: report of the definition and classification subcommittee of the international dry eye workshop (2007). Ocul Surf 2007;5:75-92.


12) Bron AJ, de Paiva CS, Chauhan SK, et al. TFOS DEWS II pathophysiology report. Ocul Surf 2017;15:438-510.


13) Stevenson W, Chauhan SK, Dana R. Dry eye disease: an immunemediated ocular surface disorder. Arch Ophthalmol 2012;130:90-100.



14) Gomes JAP, Azar DT, Baudouin C, et al. TFOS DEWS II iatrogenic report. Ocul Surf 2017;15:511-38.


15) Lasagni Vitar RM, Rama P, Ferrari G. The two-faced effects of nerves and neuropeptides in corneal diseases. Prog Retin Eye Res 2022;86:100974.


16) Meseguer V, Alpizar YA, Luis E, et al. TRPA1 channels mediate acute neurogenic inflammation and pain produced by bacterial endotoxins. Nat Commun 2014;5:3125.


17) Kulka M, Sheen CH, Tancowny BP, et al. Neuropeptides activate human mast cell degranulation and chemokine production. Immunology 2008;123:398-410.



18) Micera A, Lambiase A, Bonini S. The role of neuromediators in ocular allergy. Curr Opin Allergy Clin Immunol 2008;8:466-71.


19) Hegarty DM, Tonsfeldt K, Hermes SM, et al. Differential localization of vesicular glutamate transporters and peptides in corneal afferents to trigeminal nucleus caudalis. J Comp Neurol 2010;518:3557-69.



20) He J, Bazan HE. Neuroanatomy and neurochemistry of mouse cornea. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 2016;57:664-74.



21) Byun YS, Mok JW, Chung SH, et al. Ocular surface inflammation induces de novo expression of substance P in the trigeminal primary afferents with large cell bodies. Sci Rep 2020;10:15210.



22) Lasagni Vitar RM, Barbariga M, Fonteyne P, et al. Modulating ocular surface pain through neurokinin-1 receptor blockade. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 2021;62:26.

23) Khawaja AM, Rogers DF. Tachykinins: receptor to effector. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 1996;28:721-38.


24) Suvas S. Role of substance P neuropeptide in inflammation, wound healing, and tissue homeostasis. J Immunol 2017;199:1543-52.


25) Steinhoff MS, von Mentzer B, Geppetti P, et al. Tachykinins and their receptors: contributions to physiological control and the mechanisms of disease. Physiol Rev 2014;94:265-301.



26) Gerard NP, Garraway LA, Eddy RL Jr, et al. Human substance P receptor (NK-1): organization of the gene, chromosome localization, and functional expression of cDNA clones. Biochemistry 1991;30:10640-6.


27) Maggi CA, Patacchini R, Rovero P, Giachetti A. Tachykinin receptors and tachykinin receptor antagonists. J Auton Pharmacol 1993;13:23-93.


28) Regoli D, Boudon A, Fauch├®re JL. Receptors and antagonists for substance P and related peptides. Pharmacol Rev 1994;46:551-99.

29) Russell FA, King R, Smillie SJ, et al. Calcitonin gene-related peptide: physiology and pathophysiology. Physiol Rev 2014;94:1099-142.



30) Alexander SP, Christopoulos A, Davenport AP, et al. The concise guide to pharmacology. 2017/18: G protein-coupled receptors. Br J Pharmacol 2017;174 Suppl 1(Suppl Suppl 1):S17-129.
31) Poyner DR, Sexton PM, Marshall I, et al. International union of pharmacology. XXXII. The mammalian calcitonin gene-related peptides, adrenomedullin, amylin, and calcitonin receptors. Pharmacol Rev 2002;54:233-46.


32) Gozes I, Nakai H, Byers M, et al. Sequential expression in the nervous system of C-myb and VIP genes, located in human chromosomal region 6q24. Somat Cell Mol Genet 1987;13:305-13.


33) Linder S, Barkhem T, Norberg A, et al. Structure and expression of the gene encoding the vasoactive intestinal peptide precursor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 1987;84:605-9.



34) Sol├®s-Tarr├®s I, Cabezas-Llobet N, Vaudry D, Xifr├│ X. Protective effects of pituitary adenylate cyclase-activating polypeptide and vasoactive intestinal peptide against cognitive eecline in neurodegenerative diseases. Front Cell Neurosci 2020;14:221.


35) Harmar AJ, Fahrenkrug J, Gozes I, et al. Pharmacology and functions of receptors for vasoactive intestinal peptide and pituitary adenylate cyclase-activating polypeptide: IUPHAR review 1. Br J Pharmacol 2012;166:4-17.



36) Tatemoto K. Neuropeptide Y: complete amino acid sequence of the brain peptide. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 1982;79:5485-9.



37) Tatemoto K, Carlquist M, Mutt V. Neuropeptide Y--a novel brain peptide with structural similarities to peptide YY and pancreatic polypeptide. Nature 1982;296:659-60.


38) Gray TS, Morley JE. Neuropeptide Y: anatomical distribution and possible function in mammalian nervous system. Life Sci 1986;38:389-401.


39) Pedragosa-Badia X, Stichel J, Beck-Sickinger AG. Neuropeptide Y receptors: how to get subtype selectivity. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne) 2013;4:5.



40) M├╝ller LJ, Marfurt CF, Kruse F, Tervo TM. Corneal nerves: structure, contents and function. Exp Eye Res 2003;76:521-42.


41) Launay PS, Godefroy D, Khabou H, et al. Combined 3DISCO clearing method, retrograde tracer and ultramicroscopy to map corneal neurons in a whole adult mouse trigeminal ganglion. Exp Eye Res 2015;139:136-43.


42) Figueira L, Janeiro C, Ferreirinha F, et al. Regulation of corneal noradrenaline release and topography of sympathetic innervation: functional implications for adrenergic mechanisms in the human cornea. Exp Eye Res 2018;174:121-32.


43) Steinman L. Elaborate interactions between the immune and nervous systems. Nat Immunol 2004;5:575-81.


44) Al-Aqaba MA, Dhillon VK, Mohammed I, et al. Corneal nerves in health and disease. Prog Retin Eye Res 2019;73:100762.


45) Hwang DD, Lee SJ, Kim JH, Lee SM. The role of neuropeptides in pathogenesis of dry dye. J Clin Med 2021;10:4248.



46) Yu M, Lee SM, Lee H, et al. Neurokinin-1 receptor antagonism ameliorates dry eye disease by inhibiting antigen-presenting cell maturation and T helper 17 cell activation. Am J Pathol 2020;190:125-33.



47) Liu L, Dana R, Yin J. Sensory neurons directly promote angiogenesis in response to inflammation via substance P signaling. FASEB J 2020;34:6229-43.


48) Taketani Y, Marmalidou A, Dohlman TH, et al. Restoration of regulatory T-cell function in dry eye eisease by antagonizing substance P/neurokinin-1 receptor. Am J Pathol 2020;190:1859-66.


49) Lee SJ, Im ST, Wu J, et al. Corneal lymphangiogenesis in dry eye disease is regulated by substance P/neurokinin-1 receptor system through controlling expression of vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 3. Ocul Surf 2021;22:72-9.


50) Yang L, Sui W, Li Y, et al. Substance P inhibits hyperosmotic stress-induced apoptosis in corneal epithelial cells through the mechanism of Akt activation and reactive oxygen species scavenging via the neurokinin-1 receptor. PLoS One 2016;11:e0149865.



51) Lim JE, Chung E, Son Y. A neuropeptide, substance-P, directly induces tissue-repairing M2 like macrophages by activating the PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway even in the presence of IFN╬│. Sci Rep 2017;7:9417.



52) Konttinen YT, Hukkanen M, Kemppinen P, et al. Peptide-containing nerves in labial salivary glands in Sj├Čgren's syndrome. Arthritis Rheum 1992;35:815-20.


53) T├Črnwall J, Uusitalo H, Hukkanen M, et al. Distribution of vasoactive intestinal peptide (VIP) and its binding sites in labial salivary glands in Sj├Čgren's syndrome and in normal controls. Clin Exp Rheumatol 1994;12:287-92.

54) Batbayar B, Nagy G, K├Čvesi G, et al. Morphological basis of sensory neuropathy and neuroimmunomodulation in minor salivary glands of patients with Sj├Čgren's syndrome. Arch Oral Biol 2004;49:529-38.


55) Stern ME, Gao J, Siemasko KF, et al. The role of the lacrimal functional unit in the pathophysiology of dry eye. Exp Eye Res 2004;78:409-16.


56) Pflugfelder SC, Jones D, Ji Z, et al. Altered cytokine balance in the tear fluid and conjunctiva of patients with Sj├Čgren's syndrome keratoconjunctivitis sicca. Curr Eye Res 1999;19:201-11.


57) Lambiase A, Micera A, Sacchetti M, et al. Alterations of tear neuromediators in dry eye disease. Arch Ophthalmol 2011;129:981-6.


58) Colorado LH, Markoulli M, Edwards K. The relationship between corneal dendritic cells, corneal nerve morphology and tear inflammatory mediators and neuropeptides in healthy individuals. Curr Eye Res 2019;44:840-8.


59) Markoulli M, Colorado LH, Edwards K. The relationship between corneal nerve morphology and inflammatory mediators and neuropeptides in healthy individuals. Optom Vis Sci 2020;97:145-53.


60) Yamada M, Ogata M, Kawai M, Mashima Y. Decreased substance P concentrations in tears from patients with corneal hypesthesia. Am J Ophthalmol 2000;129:671-2.


61) Yamada M, Ogata M, Kawai M, et al. Substance P and its metabolites in normal human tears. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 2002;43:2622-5.

62) Tummanapalli SS, Willcox MDP, Issar T, et al. Tear film substance P: a potential biomarker for diabetic peripheral neuropathy. Ocul Surf 2019;17:690-8.


63) Yang LWY, Mehta JS, Liu YC. Corneal neuromediator profiles following laser refractive surgery. Neural Regen Res 2021;16:2177-83.



64) Mertaniemi P, Yl├żtupa S, Partanen P, Tervo T. Increased release of immunoreactive calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP) in tears after excimer laser keratectomy. Exp Eye Res 1995;60:659-65.


65) Gao S, Li S, Liu L, et al. Early changes in ocular surface and tear inflammatory mediators after small-incision lenticule extraction and femtosecond laser-assisted laser in situ keratomileusis. PLoS One 2014;9:e107370.



66) Chao C, Stapleton F, Zhou X, et al. Structural and functional changes in corneal innervation after laser in situ keratomileusis and their relationship with dry eye. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol 2015;253:2029-39.


67) Chao C, Golebiowski B, Zhao X, et al. Long-term effects of LASIK on corneal innervation and tear neuropeptides and the associations with dry eye. J Refract Surg 2016;32:518-24.


68) Gong X, Ren Y, Fang X, et al. Substance P induces sympathetic immune response in the contralateral eye after the first eye cataract surgery in type 2 diabetic patients. BMC Ophthalmol 2020;20:339.



69) L├│pez-de la Rosa A, Garc├Ła-V├Īzquez C, Fern├Īndez I, et al. Substance P level in tears as a potential biomarker for contact lens discomfort. Ocul Immunol Inflamm 2021;29:43-56.


70) Golebiowski B, Chao C, Stapleton F, Jalbert I. Corneal nerve morphology, sensitivity, and tear neuropeptides in contact lens wear. Optom Vis Sci 2017;94:534-42.


71) Ben├Łtez del Castillo JM, Wasfy MA, Fernandez C, Garcia-Sanchez J. An in vivo confocal masked study on corneal epithelium and subbasal nerves in patients with dry eye. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 2004;45:3030-5.





 PDF Links
PDF Links PubReader
PubReader ePub Link
ePub Link Full text via DOI
Full text via DOI Download Citation
Download Citation Print
Print